
Obesity worldwide health and medical information
Obesity
The American Medical Association classified obesity as a disease. Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index, a measurement obtained by dividing a person's weight by the square of the person's height, is over 30 kg/m2, with the range 25 - 30 kg/m2 defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values. Obesity increases the likelihood of various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritis and depression.
Obesity is most commonly caused by a combination of excessive food intake, lack of physical activity, and genetic susceptibility. A few cases are caused primarily by genes, endocrine disorders, medications, or mental disorder. The view that obese people eat little yet gain weight due to a slow metabolism is not generally supported. On average, obese people have a greater energy expenditure than their normal counterparts due to the energy required to maintain an increased body mass.
Obesity is mostly preventable through a combination of social changes and personal choices. Changes to diet and exercising are the main treatments. Diet quality can be improved by reducing the consumption of energy-dense foods, such as those high in fat and sugars, and by increasing the intake of dietary fiber. Medications may be used, along with a suitable diet, to reduce appetite or decrease fat absorption. If diet, exercise, and medication are not effective, a gastric balloon or surgery may be performed to reduce stomach volume or length of the intestines, leading to feeling full earlier or a reduced ability to absorb nutrients from food.
Obesity is a leading preventable cause of death worldwide, with increasing rates in adults and children. In 2015, 600 million adults (12%) and 100 million children were obese. Obesity is more common in women than men. Authorities view it as one of the most serious public health problems of the 21st century. Obesity is stigmatized in much of the modern world (particularly in the Western world), though it was seen as a symbol of wealth and fertility at other times in history and still is in some parts of the world.
Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps
The Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps for all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories are releases each year. The maps show self-reported adult obesity prevalence by race, ethnicity, and location. The data comes from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, an on-going state-based, telephone interview survey. The maps show that obesity impacts some groups more than others. There are notable differences by race and ethnicity, as shown by combined data from last years:
- 2 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic white adults.
- 9 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among Hispanic adults.
- 29 states and the District of Columbia had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic black adults.
Obesty By Education and Age
- Obesity decreased by level of education. Adults without a high school degree or equivalent had the highest self-reported obesity (35.0%), followed by high school graduates (33.1%), adults with some college (33.0%) and college graduates (24.7%).
- Young adults were half as likely to have obesity as middle-aged adults. Adults aged 18-24 years had the lowest self-reported obesity (18.1%) compared to adults aged 45-54 years who had the highest prevalence (36.9%).
Obesty Across States and Territories
Prevalence of Self-Reported Obesity Among U.S. Adults by State and Territory.
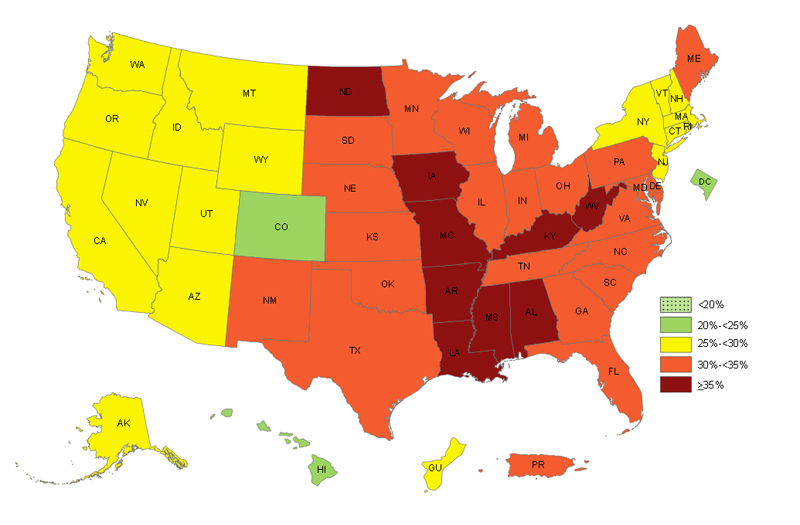
- All states and territories had more than 20% of adults with obesity.
- 20% to less than 25% of adults had obesity in 2 states (Colorado and Hawaii) and the District of Columbia.
- 25% to less than 30% of adults had obesity in 17 states and Guam.
- 30% to less than 35% of adults had obesity in 22 states and Puerto Rico.
- 35% or more adults had obesity in 9 states (Alabama, Arkansas, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, and West Virginia).
- The South (33.6%) and the Midwest (33.1%) had the highest prevalence of obesity, followed by the Northeast (28.0%), and the West (26.9%).
Obesity Treatment
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. Obesity isn't just a cosmetic concern. It is a medical problem that increases your risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.
Overweight and obesity are major risk factors for a number of chronic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Once considered a problem only in high income countries, overweight and obesity are now dramatically on the rise in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban settings.
There are many reasons why some people have difficulty avoiding obesity. Usually, obesity results from a combination of inherited factors, combined with the environment and personal diet and exercise choices.
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. A crude population measure of obesity is the body mass index (BMI), a person’s weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of his or her height (in metres). A person with a BMI of 30 or more is generally considered obese. A person with a BMI equal to or more than 25 is considered overweight.
The good news is that even modest weight loss can improve or prevent the health problems associated with obesity. Dietary changes, increased physical activity and behavior changes can help you lose weight. Prescription medications like Xenical (Orlistat) and weight-loss procedures are additional options for treating obesity.
Research
Obesity Management Market Research Report
Related
Buy Xenical Orlistat
Categories
- Allergy
- Alcohol Addiction
- Anxiety
- Cardiology
- Depression
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Phlebology
- Diabetes
- Herpes Viruses
- Gastroenterology
- General Health
- Gerontology
- Hematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Men's Health
- Neurology
- Obesity
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics & Sports Medicine
- Parasitic Diseases
- Pediatrics
- Psychiatry
- Radiology
- Respiratory
- Rheumatology
- Smoking Cessation
- Urology
- Women's Health